
Table Of Contents
- What Is The Racial Justice Movement?
- You Must Have Heard Of White
- What Is The Purpose Of This Movement?
- The People Behind The Movement
- Wilberforce And Eiquano
- Nelson Mandela
- The 21st Century Movement For Racial Justice
- Black Lives Matter
- Racial Justice In The Latin and the Hispanic Community
- Racial Justice In The Asian Community
- Laws And Court Ruling In Support Of The Racial Justice Movement
- The Civil Rights Act of 1964
- Voting Right Act
- The Fair Housing Act of 1968
- The Equal Credit Opportunity Act (ECOA) Of 1974
- Indian Self-Determination And Education Assistance Act (Isdeaa) Of 1975
- The Hate Crimes Prevention Act Of 2009
- Steps Taken By The Biden Administration To Combat Racism
- Final Word
A Fight Against Racism: The Racial Justice Movement
The racial justice movement aims to bring about racial equity and end discrimination.
“I have a dream that one day this nation will rise up and live out the true meaning of its creed: ‘We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal.’
I have a dream that one day, on the red hills of Georgia, the sons of former slaves and the sons of former slave owners will be able to sit down together at the table of brotherhood.
…. I have a dream that my four little children will one day live in a nation where they will not be judged by the color of their skin but by the content of their character.”
This is the iconic speech delivered by Dr. Martin Luther King Junior, the father of the civil rights movement. This upholds the basic skeleton of the movement for racial justice that carries on to date.
If you are familiar with the Black Lives Matter movement- a 21st-century manifestation of the racial justice movement, you must also know where it all started. You enjoy the freedom from discrimination of all types. Today, the racial justice movement has a million advocates and supporters all over the world, especially in the United States.
So without much delay, let’s get on to the real deal.
What Is The Racial Justice Movement?

The racial justice movement is a socio-political as well as economic movement that started way back in the 18th and 19th Centuries with the abolitionist movement.
As the name suggests, the racial justice movement stands for the equal treatment of all races and ethnic groups. It is the ongoing battle for equality of all races in all spheres of life. It is essentially a battle against white privilege.
You Must Have Heard Of White

White privilege is the “unquestioned and unearned set of advantages, entitlements, benefits and choices bestowed on people solely because they are white. Generally white people who experience such privilege do so without being conscious of it.”
This movement targets government practices, attitudes, policies, and even behavior seen in society at large, targeting people of a certain race, mostly all who are not white.
What Is The Purpose Of This Movement?
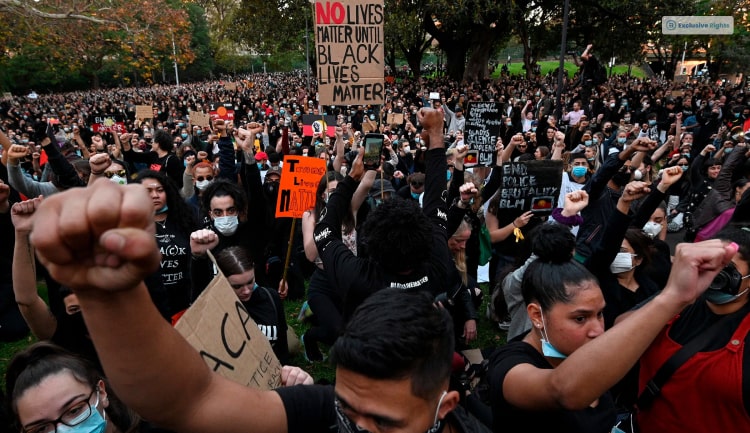
The racial justice movement aimed to do away with racism in the system of the United States. It brought equality and Justice into the educational system, criminal justice system, housing, employment, Healthcare, and many more aspects of the nation.
It was a movement against oppression. The movement was done to bring about oppressive practices to the forefront. It brought Awareness of the policy of the government that was specifically targeting marginalized communities.
Thus, to cut it short, the movement wanted to create awareness and appreciation for all races. It also wanted to bring about a change in policies of the Government and cause empowerment of these colored individuals facing discrimination on a daily basis.
The People Behind The Movement

The early supporters of this movement included O. Equiano, G. Sharp, T. Clarkson, and W. Wilberforce- from the early 18th century when the movement was budding and had some teething troubles.
Wilberforce And Eiquano
Mr. Eiquano was himself a slave once and wrote An Autobiography which counted as a powerful statement on his abolitionist mindset. All of the above the name individuals work tirelessly to end slavery and raise awareness in the community.
These people sold the seat of the movement, which later on continued in its full form.
The British Abolition Movement was a whole new deal. It all started under the leadership of the British politician W. Wilberforce. He wanted to bring an end to the slave trade existing throughout Europe to the Americas.
Next, the underground railway system was used by H. Tubman to create an elaborate network of people in support of the movement.
Soon the American aunty slavery society was established in 1833. It sought the freedom of slaves and equal rights for the former slaves.
The 19th century was also witness to the first women’s rights movement. It was an integral part of the racial justice movement. The rights of both white women and women of color were upheld in this movement.
Nelson Mandela
Nelson Mandela’s contribution to the foundation of the Racial Justice Movement was immense.
The history of the racial justice movement could go back to the Europeans, mostly the Dutch and the British population invading the South African lands for gold and diamond.
By the beginning of the 20th century, The Land Act was passed by the British colonial government. This gave the white race the upper hand, the White Privilege as we know it. They now controlled the land. The black people would, from then onward, live only on reserves.
By 1950, the Africaner National Party had established close to 350 laws that basically gave way to White Supremacy. These laws officially recognized Apartheid throughout the nation.
All of South Africa was divided into racial groups.
- Interracial marriage and mingling were completely banned.
- The right to vote was taken away from the black population.
- Many protestors and advocates of the racial justice movement were killed during this time period. Nelson Mandela finally brought an end to the culture of apartheid in South Africa in the year 1994.
The 21st Century Movement For Racial Justice
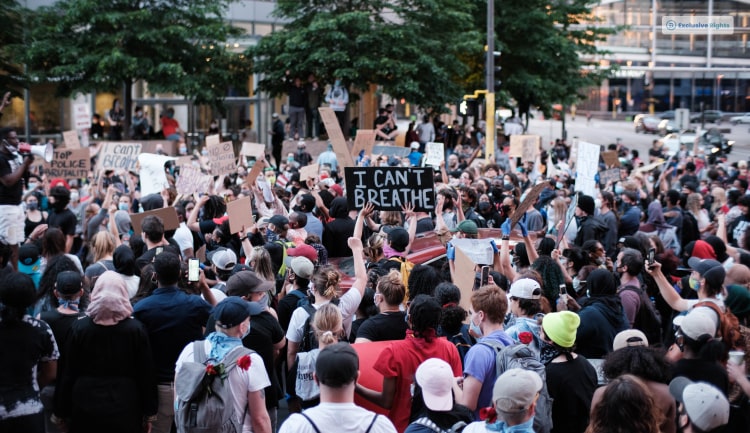
Let us see how different marginalized communities were affected by racism and how they took steps to combat it.
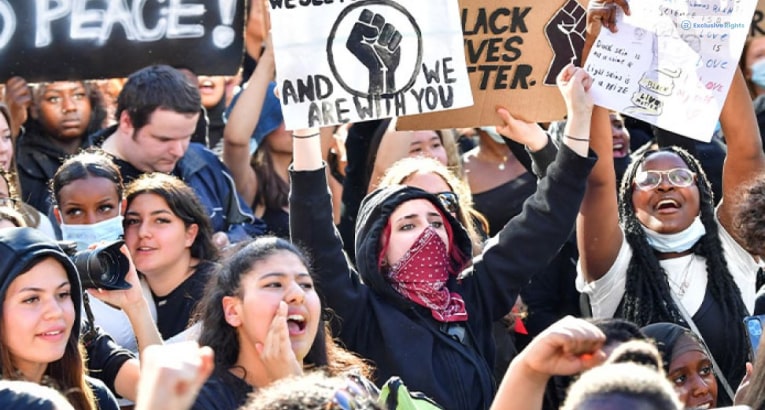
Black Lives Matter
The Black Lives Matter Movement is something that most of us are familiar with. It started mostly as a social justice movement that later on became the flag bearer for the racial just movement of the 21st century. However, there are a few precursors to the famous BLM.
The racial justice movement and criminal justice reform go hand in hand. The foundation of this goes way back to the 1970s. President Nixon had just declared drugs to be the number one public enemy. The impoverished black and Hispanic population of the United States, so 80% of the users are black, all from the Latino communities. This led to a marked increase in police violence against these groups. Racial youth, first-time users, and petty offenders were being given lifelong or decades-long sentences for possession of even small amounts of drugs.
A black national was 3.6 times more likely to get arrested for having marijuana in possession as compared to a white individual- As reported by ACLU.
Alicia Garza and two other black activists spearheaded the Black Lives Matter movement after police oppression and harassment became a regular occurrence in the Black community of America. Although the movement was founded way back in 2013, it has gained quite some prominence due to George Floyd’s murder by the police. George Floyd was a black American who was arrested on suspicions of theft. However, the arresting officials needed down on his neck long enough to cut off his air supply, after which he died. “I can’t breathe” was what he kept repeating until he died out of suffocation.
The “Black Lives Matter” movement gained visibility and recognition throughout the US and globally after George Floyd’s death.
The movement still continues to function as a wing of the racial justice movement to bring racism to an immediate end and bring about police reform.
Racial Justice In The Latin and the Hispanic Community

On a daily basis, these communities face immigration-related challenges and various other forms of racial discrimination and marginalization. Latin and Hispanic activists have also played a very important role in the racial justice movement in the United States.
Not just the black community but the Hispanic population was also heavily affected by systemic racism. Unequal wages, losses of pay, derogatory treatment, racial slurs, and prejudice in all spheres of life- they face it all. Discontent has been a recurring issue in the Hispanic community throughout the American timeline. This negative when it comes to the Asian race has been seen in educational institutions, economic fears, and on a societal level as well. Recently a study was conducted by Pew Research Centre that showed a high level of dissatisfaction in the country among the Hispanic population.
This community has also felt that immigration and economy-related issues at the most pressing ones in the nation.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the number of Hispanic students that graduated from high school is less than 30%.
This community has also brought to notice the discrimination in working conditions that they face on a daily basis. A study conducted states that these conditions could lead to a lack of self-confidence as well as withdrawal from work together.
This part of the US population has therefore shown that they stand with the Black Lives Matter movement.
Many have also stepped up for immigration rights, social equity, and economic justice. Apart from advocating against police violence for equal educational and economic opportunities, musicians, artists, and writers have used cultural and creative platforms to spread awareness for racial justice. The Mexican Painter Freida Kahlo has become a popular symbol for Hispanic rights and feminism.
Racial Justice In The Asian Community
The Asian Community is collectively called the Asian American and Pacific Islanders. This part of the American population is used to battling racism, racial stereotyping, hate crimes, and xenophobia on a daily basis.
Throughout history, they have been blamed for economic challenges. For instance, the entry of Japanese automakers into the U.S. market had a huge impact on the auto industry. For this, Asians, no matter their country of origin, started being victims of hate crimes throughout the USA.
The racism and injustice faced by this community is marked by a series of indeed unfortunate events. It all started when the Chinese Exclusion at was brought into the system back in 1882. Chinese laborers who had fled the country to avoid persecution were banned from entering the United States. The USA’s stance against Communism led to this unwelcoming behavior. This did not end with the act. Chinese laborers were also unfairly treated along the West Coast. They were paid chronically low wages and were rejected from jobs even after they were eligible and qualified.
This pattern returned 100 years later to the United States. Asian Americans were targeted for being “smarter” than the average white American. They faced hostilities for stealing jobs from White Americans.
In 1982, Vincent Chin, a 27-year-old Chinese American, tragically lost his life in Detroit. He was killed by two white men – one being a Chrysler worker and the other recently laid off from Chrysler. A witness recounted that they used offensive language while wrongly assigning blame to him for their employment difficulties.
The racial justice movement has been actively incorporated by the activists of this community. They have fought to bring about awareness about their language and culture. These activists have also stood in solidarity with the Black Lives Matter movement.
Laws And Court Ruling In Support Of The Racial Justice Movement
So far, we have talked all about the history and the reasons behind the movement. Now it’s time we discuss the effect and the laws that were established as a result of this movement.
Several laws in the United States have been enacted to stop racial discrimination and promote racial justice. These laws address systemic racism and protect the civil rights of marginalized communities. These are designed to address discrimination, unequal treatment, and racial injustice
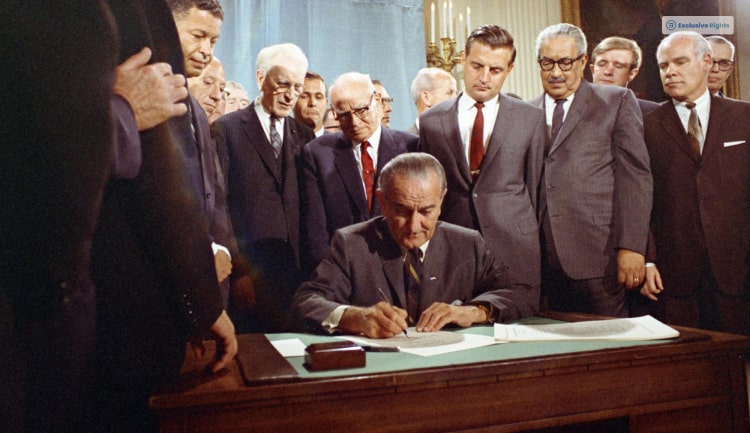
The Civil Rights Act of 1964
This Act came into force in the year 1964. It criminalized discrimination based on
race, color, language spoken, culture or national origin in public spaces, places of employment, and institutions of education in the United States.
By virtue of this Act, the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) was set up to inquire into instances of discrimination and further the racial justice movement.
Black people have, throughout history, endured societal prejudice. Their loyalty has been called to question. They’ve been called “kook”s and “criminals” by their skin color alone. The Jim Crow time period saw white workers receive way more wages than black ones. In and around the second world war, Asians, particularly Japanese immigrants, faced a huge loss of employment in the United States.
Time and again, migrant workers have faced poor and inhuman working conditions. The Equal Employment Opportunity Commission looks into any further incidents of a similar nature and sees to it that the racial justice movement reaches its goal.
Voting Right Act

The Voting Rights Act of 1965 is a major contributor to the racial justice movement. It targets racial discrimination in voting practices in the US. The immigrant communities and black parts of the population suffer from low literacy rates and economic challenges. However, Education is, after all, subjective.
The colonists often tried to weaponize literacy tests to keep marginalized communities from taking part in the voting process. This legislation therefore prevents such targeted behaviour from stopping minority voters take part in the democratic process.
The Fair Housing Act of 1968

This Act prohibits all US nationals from discriminating against individuals based on their race, color, culture, national origin, culture, and a number of other protected characteristics. This act was passed because earlier, people of color were often only permitted to settle down in certain parts of the town, commonly called the “hood” or the neighborhood. If these people ever dared to settle in the commonly known “white territories,” they faced immense persecution and boycott. This Act helped American soil be equally open to all its nationals, irrespective of their color. Thus it was an integral part of the racial justice movement.
The Equal Credit Opportunity Act (ECOA) Of 1974

This Act addressed all concerns where certain racial communities, the typically non-white population, were denied loans and credits just on the basis of their race. It specifically prohibits “credit discrimination” on the basis of race, color, religion, national origin, sex, marital status, age, or the receipt of public assistance.
Indian Self-Determination And Education Assistance Act (Isdeaa) Of 1975
This law grants Native American tribes greater control over their own affairs, including education and healthcare, to address historical injustices. The United States Congress brought the Indian Self-determination and Education Assistance Act in the year 1975.
It would include the territories of the 15 tribal organizations, primarily from Nebraska, North Dakota, and South Dakota. It was enacted to make sure that Indian tribes, who had been long suffering under the European colonist rule, finally attend freedom and autonomy over there is territory. This Act gave the community the freedom to use Federal funds however they best saw fit. Only the Indian tribes could decide the direction for the services the Federal government would provide them.
- The Indian tribes would enter into contracts with the Bureau of Indian Affairs for Federal programs and services.
- All Construction projects would be three approved by the tribes.
- And oversight of audits would be submitted by the tribes.
- All sorts of technical assistance required would be given to the Tribes of the region.
This was a step toward the racial justice movement through which the native population felt empowered.
The Hate Crimes Prevention Act Of 2009

The hate crimes prevention act of 2009 is also known as the Mathew Shepherd and James Byrd Jr hate crimes prevention act of 2009. It was brought into force by the National Defence Authorization Act in 2010. It was enacted solely to investigate and take action against hate crimes against a person due to their “perceived” race, color, religion, gender, sexual orientation, gender identity, and disability. The act punishes:
- The person committing any violent act that results in bodily injury
- A person who uses fire explosives, firearms, or incendiary devices to harm others based on the protected characteristics
- Or anyone that threatens violence, physical injury, or other hate crimes.
Therefore, this act is a direct step in the protection of racial justice.
Steps Taken By The Biden Administration To Combat Racism

The current government claims to have taken quite a few steps to battle systemic racism. The official website of the White House gives a list of some distinct efforts taken as President Biden took office. Let’s have a look at some of them.
- Systemic racism has been a political problem in the United States. These practices have apparently contributed to increasing health disparities, increase in wealth gaps, and also various other inequalities in the system.
- President Biden apparently issued an executive order to combat it. Through this order, the government would take an approach to create opportunities for communities that have suffered so far.
- A memorandum was issued that attacked practices of intolerance towards Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders, targeted xenophobia, and combat racism. Active steps were taken so that any actions, statements, or documents issued by the Federal Government do not contribute to racism.
- The post of chief diversity and inclusion officer was created at the level of state departments. These officers report to the secretary and formulate inclusive policies. Senior members of the department are held accountable for the progress of this wing. The department promotes equity, inclusion, and diversity in the foreign policy of the United States.
- The secretary of state will report to the Congress committees on steps taken to battle ethnic discrimination abroad. The Federal government will make efforts to fund Embassy programs, issue civil society grants, and cultural exchange and leadership programs.
- The Government of the United States will work through the Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights, and Labor to fulfill these needs.
- The Federal government also makes an effort to support locally-led programs. These programs target racial and ethnic hatred. They give opportunities for victims to speak out against racism.
The United States has taken action internationally. It has joined 140 other Nations to take a global stand against racial discrimination, xenophobia, and intolerance. A representative from the US has also been nominated to the committee on the elimination of racial discrimination.
Final Word
With this, we come to the end of this piece, where we have elaborated on the various manifestations of the racial justice movement, its causes, and steps taken by the United States Government to combat racism. However, this article does not signify the end but merely the beginning. We will continue to bring you detailed accounts of the ongoing movements as and when they take place. We hope you found the article helpful and engaging! Do let us know your thoughts on it!
Read More:









